How Alcohol Can Affect Your Body
How Alcohol Can Affect Your Body: Drinking too much can impair your immune system, making your body a much easier target for disease.

Drinking excessively, whether on a single occasion or over time, can have severe consequences for your health. Here’s how alcohol can affect your body:
How Alcohol Can Affect Your Body
Brain:
Alcohol disrupts the brain's communication pathways and can alter the brain's appearance and function. These disruptions can alter one's disposition and conduct, as well as make it more difficult to think effectively and move with coordination.
Heart:
Drinking a lot over a long time or too much on a single occasion can damage the heart, causing problems including:
- Cardiomyopathy – Stretching and drooping of heart muscle
- Arrhythmias – Irregular heart beat
- Stroke
- High blood pressure
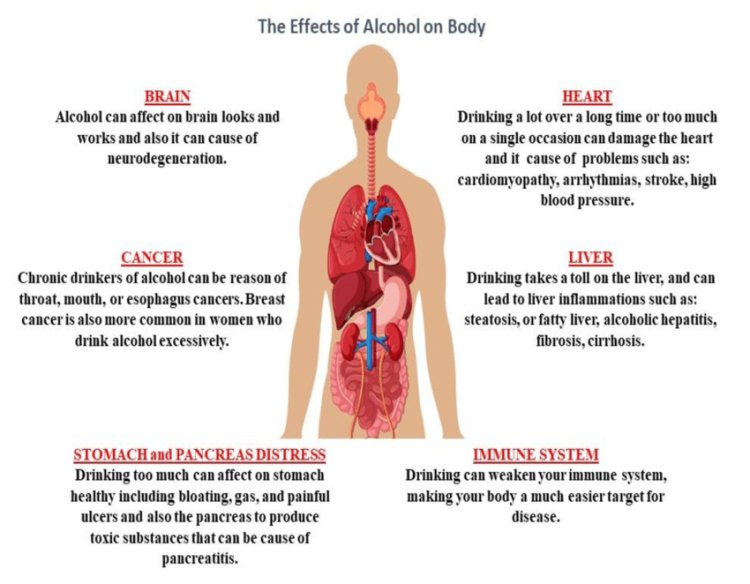
Liver:
Heavy drinking takes a toll on the liver, and can lead to a variety of problems and liver inflammations including:
- Steatosis, or fatty liver
- Alcoholic hepatitis
- Fibrosis
- Cirrhosis
Pancreas:
Alcohol can alter the structure and function of the brain by interfering with its communication pathways. These disturbances can alter mood and behavior and make it more difficult to think clearly and move with coordination.
Cancer:
National Cancer Institute: "There is a strong scientific consensus that alcohol consumption can cause multiple types of cancer." The National Toxicology Program of the United States Department of Health and Human Services lists alcohol consumption as a documented human carcinogen in its Report on Carcinogens.
"According to the evidence, a person's risk of developing an alcohol-related cancer increases with the amount of alcohol he or she consumes, particularly the amount of alcohol consumed consistently over time. Even those who consume no more than one alcoholic beverage per day and those who binge drink (consuming four or more alcoholic beverages for women and five or more for men in one session) have a modestly increased risk of developing certain cancers. Based on 2009 data, an estimated 3.5% of cancer fatalities in the United States (approximately 19,500 deaths) were attributable to alcohol use.
There are distinct correlations between alcohol consumption and the risk of developing certain forms of cancer.
Cancers of the head and neck, including those of the buccal cavity, pharynx, and larynx.
Esophageal cancer, specifically squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. In addition, alcoholics who inherit a deficiency in an enzyme that metabolizes alcohol have significantly increased risks of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
- Liver cancer.
- Breast cancer: Studies have consistently found an increased risk of breast cancer in women with increasing alcohol intake. Women who consume about 1 drink per day have a 5 to 9 percent higher chance of developing breast cancer than women who do not drink at all.
- Colorectal cancer.
Also read: Brain Fog And COVID-19: Let’s Clear The Confusion!
Immune System:Brain Fog And COVID-19: Let’s Clear The Confusion!
Drinking too much can impair your immune system, making your body a much easier target for disease. People who drink excessively are more likely to contract diseases such as pneumonia and tuberculosis than those who do not drink excessively. Drinking excessively on a single occasion impairs your body's ability to fight off infections for up to 24 hours.